Did you know that you have more fat cells in your body than the number of people living on earth right now? Fat cells exist in almost all parts of the body except the brain, eyelids and oesophagus. So instead of hating FAT, its time you start looking at some of the cold facts of FAT square in the face!
First of all, there are approximately 30-50 billion fat cells in your body -if you are a healthy adult, or anywhere between 60-100 fat cells if you are considered obese. In fact, our brain is composed of 60% fat and even though the brain is a small part of the body (2%) it uses 20% of the body’s metabolic energy!
Besides that, fat is considered to be your number one source of energy! It is in fact, essential for survival and it is a known fact that after puberty that you will NOT gain any more fat cells. So, if you any gain weight, the number of fat cells remains the same. Liposuction is the only way to physically remove fat cells.
The only thing that changes is that each fat cell expands in size- getting bigger and bigger –and can get as big as ten times its normal size. Gender and genes determine fat storage.
There is also a popular misconception that fat makes a person overweight or obese. In fact, our body’s pumps out insulin, which affects the amount of fat, we have in our body. Sugar on the other hand is the real villain, which makes us fat. It sabotages our waistlines and steals our health!
Our body pumps out more and more insulin to pull the blood sugar levels back down. It’s impossible to burn up all the sugar that we eat and inevitably our body stores it as fat and creates insulin resistance and overall metabolic havoc among other mayhem. By eating more sugar, your cells become numb to insulin’s call and more and more insulin to pull your blood-sugar levels back down.
This is possible only through the absorption of vitamins A, D, E and K. These vitamins are only soluble in fat and the only manner our body can absorb them, digest them and transport these vitamins is when they get dissolved in fat.
In fact, fat is important for a number of reasons; it protects our internal organs from external shock, helps to maintain healthy cellular functions and it helps to maintain the temperature of the body. Fat is also important to maintain healthy skin and hair.
Fat is a compound that can stay in both liquid and solid form at room temperature. It is a compound, i.e. it is a type of energy that our body requires and the other two energies are known as proteins and carbohydrates. Another term used to refer to fat and oil is lipid; lipids are nothing but fat which can be either in liquid or solid form.
There are different kinds of fats: saturated fats, unsaturated fats and trans fats. Unsaturated fats have two categories: mono unsaturated fats and polyunsaturated fats. Bad fats include saturated and trans fats. Trans fats (also known as hydrogenated fats) is all the fat that is contained in processed or manufactured foods.
Fats are also known as triglycerides and are esters of three fatty acid chains and the alcohol glycerol. Fat is an important foodstuff for many forms of life and fats serve both structural and metabolic functions. While there are many different kinds of fats, each variation is a variation on the same chemical structure. All fats are derivatives of fatty acids and glycerol. Most fats are glycerides.
While growing up, I was early to encounter many chronic diseases like asthma, diabetes, heart diseases and even cancer; but I have never related them to body fat or even obesity, until now! Due to its high caloric value (1 gram of fat =9 calories) it is very easy to consume more calories than required.
These extra calories, which get stored in your body as fat lead to weight gain and it is the liver that is responsible for producing cholesterol, which is important for a healthy body and is a building block for other essential chemicals that the body produces.
Obesity is a massive public problem and not maintaining a healthy weight for your height can adversely affect you leading to gallstones, some cancers, diabetes and coronary heart disease.
What is cholesterol?
Cholesterol is a waxy substance that in low levels flows freely around the body in the blood. Cholesterol is actually required by the body and is a building block in cell membranes. It helps in making certain hormones that play a crucial role spermatogenesis (the process of sperm production). While only 20% comes from our food, about 80 % is expected to be produced by the liver.
Higher levels of cholesterol mean a higher risk of developing coronary heart disease.
As we go through our middle years, the proportion of fat to body weight tends to increase more and more. This gap tends to increase more in women than men and all the extra pounds park themselves bang around the midsection of the body.
At times we may have to accept all of these changes as inevitable ones – as they are all apart of ageing, but adopting a wholesome lifestyle and diet certainly is a healthier way to live. Cholesterol is carried around the body in the bloodstream combined with proteins, known as lipoproteins.
There are two main types of lipoproteins that are used to measure the cholesterol level in the blood – LDL – low-density lipoprotein and HDL – High-density lipoprotein. Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) is often called ‘bad’ cholesterol whereas high-density lipoprotein (HDL) is considered ‘good’ cholesterol. HDL is ‘good’ as it can remove extra bad cholesterol from the bloodstream.
People who have high cholesterol levels are more likely to develop health problems, the risks are increased further for people who also smoke, have high blood pressure, are physically inactive or unfit, are overweight or obese or suffer from diabetes.
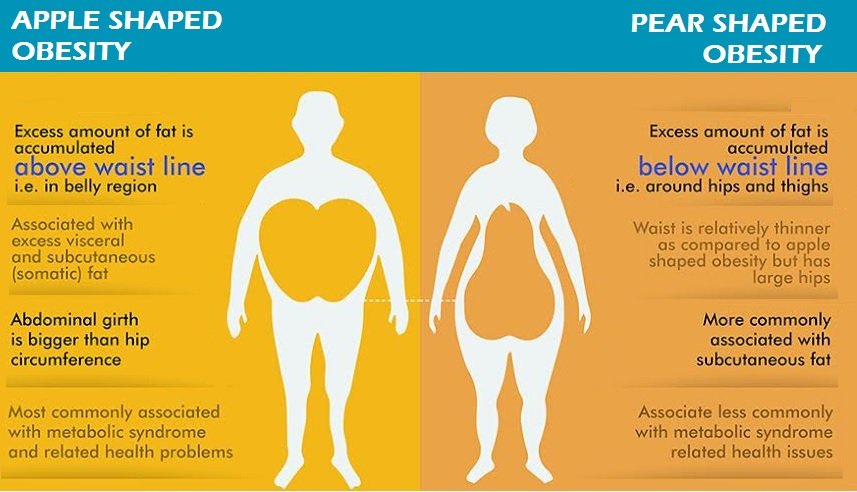
Abdominal or visceral fat is known to be the worst type of fat that you can have. It is the fat that is stored in your abdominal cavity; therefore stored more around a number of internal organs such as the liver, pancreas and intestines. If you have a high amount of visceral fat you are more likely to be at risk of catching any of the chronic diseases such as heart diseases, high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes. For optimum health your visceral fat should be beneath 13.
